How each of the Network Protocol layers work behind the scene
When we type google.com in our browser, we see the google home page. We are unaware of the back scene about how the each layer of the protocol works. In this post i will describe, how each of the protocol layer works.
First of all let’s see what are the layers involved in OSI and TCP/IP protocols.
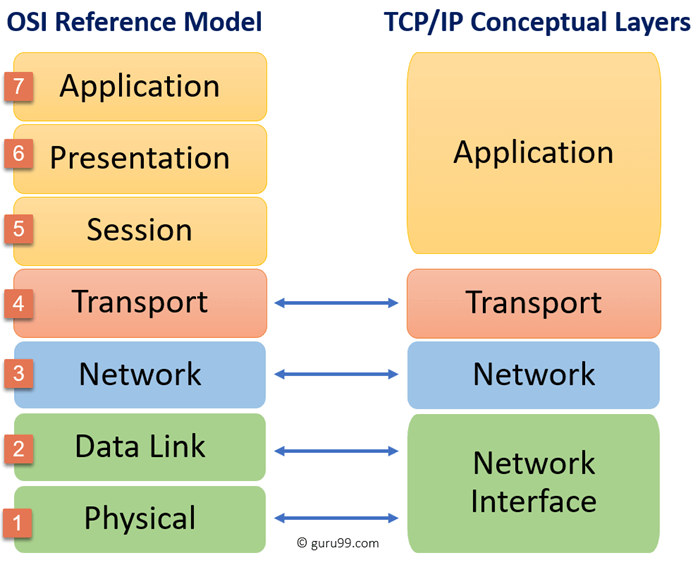
Layers and their functions of OSI model
| Layer | Task At Layer |
|---|---|
| Application Layer | Web browser that the user interacts with. (Google Chrome) |
| Presentation Layer | It takes care of syntax and semantics of the information that is exchanged between two systems. (Encryption and Decryption, Data Compression) |
| Session Layer | It establishes, manages and terminates the communication session. (Response Time) |
| Transport Layer | Segments and Reassemble the message, Adds port address, Connection control (TCP or UPD), Flow Control, Error control |
| Network Layer | Moving the packets from source to destination through routing. (Add IP Address to header) |
| Data Link Layer | - Defines the format of the data in the network, - Responsible for uniquely identify devices on the network, - (Adds MAC address and Logic link control LLC) |
| Physical Layer | - Transmit the bits from one node to another., - It establishes, maintains and terminates the physical connection., - It specifies what sort of media is used for transmission, this may includes cable type, radio frequency |
Layers and their functions of TCP/IP model
| Layer | Task At Layer |
|---|---|
| Application Layer | - User interact with the application, - Uses HTTP, FTP, Telnet |
| Transport Layer | - Responsible for reliable, flow control and error correction, - Uses either TCP or UDP |
| Network Layer or Internet Layer | - Transmission of packets, - IP, ARP and ICMP |
| Network Interface Layer | - How the data is to be send from the physical layer |